大蒜是我们饮食中必不可少的食材,大蒜中含有抗氧化物质,能起到抗衰老的作用。最近的研究更是表明,从饮食中摄入含烯丙基硫化物的大蒜有助于保持健康的肠道微生物,并能改善老年人的认知健康。
关键词:科普、译文、大蒜
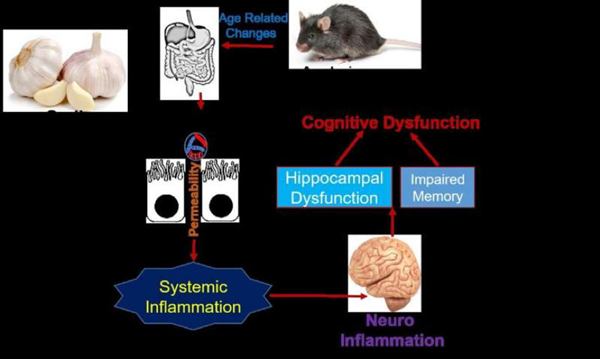
[Oral allyl sulfide administration reduces the age-related memory problem through restoration gut bacteria in the intestine (rNDNF= recombinant neuronal-derived natriuretic factor). Credit: Neetu Tyagi and Jyotirmaya Behera]
[口服烯丙基硫化物可以通过修复肠道细菌(rNDNF=重组神经元源性利钠因子),减少与年龄相关的记忆问题。资料来源:Neetu Tyagi和Jyotirmaya Behera]
Consuming garlic helps counteract age-related changes in gut bacteria associated with memory problems, according to a new study conducted with mice. The benefit comes from allyl sulfide, a compound in garlic known for its health benefits.
根据一项对小鼠进行的新研究,食用大蒜有助于抵消与记忆问题相关的肠道细菌的年龄变化。这种益处来自于烯丙基硫化物,它是大蒜中的一种化合物,以有益健康而闻名。
'Our findings suggest that dietary administration of garlic containing allyl sulfide could help maintain healthy gut microorganisms and improve cognitive health in the elderly,' said Jyotirmaya Behera, Ph.D., who lead the research team with Neetu Tyagi, Ph.D., both from University of Louisville.
“我们的研究结果表明,从饮食中摄入含烯丙基硫化物的大蒜有助于保持健康的肠道微生物,并能改善老年人的认知健康,”Jyotirmaya Behera博士说,他和路易斯维尔大学的Neetu Tyagi博士共同领导了这个研究小组。
Behera will present the research at the American Physiological Society's annual meeting during the 2019 Experimental Biology meeting to be held April 6-9 in Orlando, Fla.
Behera将在2019年4月6日至9日在佛罗里达州奥兰多举行的实验生物学会议期间的美国生理学会的年会上展示这项研究。
The gut contains trillions of microorganisms collectively referred to as the gut microbiota. Although many studies have shown the importance of these microorganisms in maintaining human health, less is known about health effects linked to gut microbiota changes that come with age.
肠道含有数万亿微生物,统称肠道微生物群。尽管许多研究已经证明了这些微生物在维持人类健康方面的重要性,但人们对随着年龄增长而引起的肠道微生物群变化所带来的健康影响知之甚少。
'The diversity of the gut microbiota is diminished in elderly people, a life stage when neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's develop and memory and cognitive abilities can decline,' said Tyagi. 'We want to better understand how changes in the gut microbiota relate to aging-associated cognitive decline.'
“老年人肠道微生物群的多样性在减少,这是阿尔茨海默氏症和帕金森氏症等神经退行性疾病发展,记忆和认知能力下降的生命阶段,”Tyagi说。“我们希望更好地了解肠道微生物群的变化与衰老相关的认知能力下降之间的关系。”
For the study, the researchers gave oral allyl sulfide to mice that were 24 months old, which correlates to people between 56 and 69 years of age. They compared these mice with 4- and 24-month-old mice not receiving the dietary allyl sulfide supplement.
在这项研究中,研究人员给24个月大的小鼠口服烯丙基硫化物,这大约是人类的56至69岁。他们将这些小鼠与未接受膳食烯丙基硫化物补充的4个月和24个月大的小鼠进行了比较。
The researchers observed that the older mice receiving the garlic compound showed better long- and short-term memory and healthier gut bacteria than the older mice that didn't receive the treatment. Spatial memory was also impaired in the 24-month-old mice not receiving allyl sulfide.
研究人员观察到,接受大蒜化合物的老年小鼠比没有接受这种物质的老年小鼠显示出了更好的长期和短期记忆力以及拥有更健康的肠道细菌。在没有接受烯丙基硫化物的24个月大的小鼠中,空间记忆也受到了损害。
Additional experiments revealed that reduced gene expression of neuronal-derived natriuretic factor (NDNF) in the brain was likely responsible for the cognitive decline. This gene was recently discovered by the University of Louisville researchers and is required for long-term and short-term memory consolidation.
另外的实验表明,大脑中神经元衍生的利钠因子(NDNF)基因表达水平的降低可能是认知能力下降的原因。该基因最近由路易斯维尔大学的研究人员发现,是巩固长期和短期记忆所必需的。
The researchers found that mice receiving the garlic compound exhibited higher levels of NDNF gene expression. In addition, recombinant-NDNF protein therapy in the brain restored the cognitive abilities of the older mice that did not receive the garlic compound. The researchers also found that oral allyl sulfide administration produces hydrogen sulfide gas—a messenger molecule that prevents intestinal inflammation—in the gut lumen.
研究人员发现,接受大蒜化合物的小鼠表现出更高水平的NDNF基因表达。此外,在大脑中的重组 - NDNF蛋白疗法恢复了没有接受大蒜化合物的老年小鼠的认知能力。研究人员还发现,口服烯丙基硫化物会在肠道内产生硫化氢气体,这是一种可以预防肠道炎症的信使分子。
Overall, the new findings suggest that dietary allyl sulfide promotes memory consolidation by restoring gut bacteria. The researchers are continuing to conduct experiments aimed at better understanding the relationship between the gut microbiota and cognitive decline and are examining how garlic might be used as a treatment in the aging human population.
总的来说,新发现表明饮食中的烯丙基硫化物通过恢复肠道细菌促进记忆巩固。研究人员正在继续进行实验,目的是更好地了解肠道微生物群与认知能力下降之间的关系,并研究大蒜如何用于老年人群的治疗。
(责任编辑:周姚)
(版权说明,转载自:微信公众号:科学猫科普)

